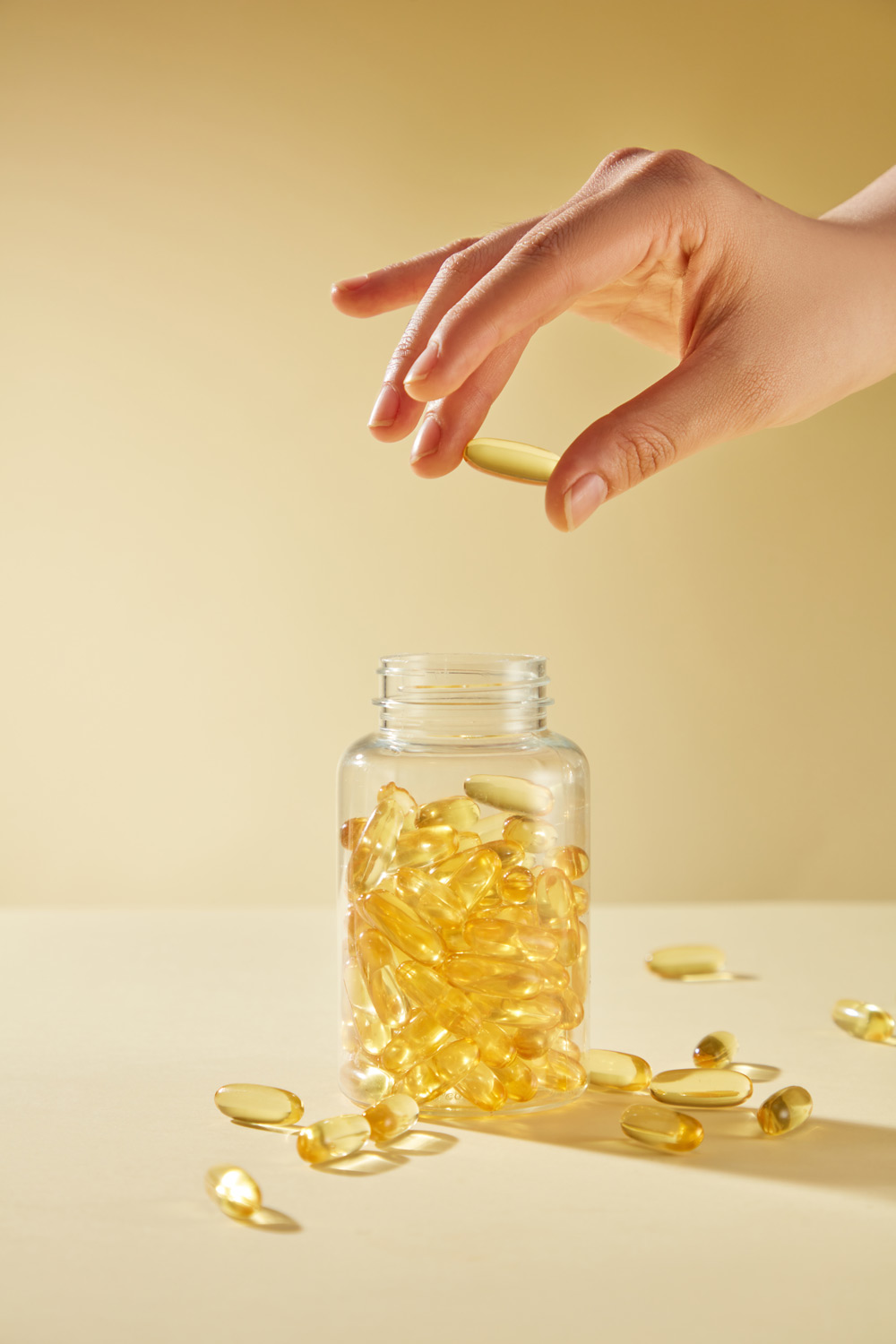
Daily Fish Oil May Slow Down Ageing
By
2 months ago
Omega-3s may be even more important than we thought
Omega-3s – the fatty acids found in certain fish, nuts and seeds – have long been lauded for their health benefits, from boosting brain function to reducing inflammation in the body. And now new research suggests the essential nutrient may also have the power to slow down the ageing process.
Study Finds Omega-3s Could Boost Healthspan
A major clinical trial, published in Nature Aging, explored whether certain interventions can extend humans’ healthspan, the period of your life which you spend healthy before declining in old age. The trial involved 777 participants aged over 70 from Switzerland, who were tracked across a three-year period.
Researchers found older people who took one gram of omega-3s every day had aged three months less than others on the trial, with the ageing rate determined using advanced biological tools called epigenetic clocks. Those who also exercised regularly and took vitamin D supplements showed even less signs of ageing.
Heike Bischoff-Ferrari, a clinician-scientist at the University of Zurich and one of the lead authors in the study, said: ‘Omega-3 plays on multiple pathways of ageing, such as being anti-inflammatory. Similarly, vitamin D and exercise have multiple benefits. We thought, if you play on each of these differential pathways, do you get an additive benefit?’
She continued: ‘While the effects may appear small with three to four months rejuvenation of biological age in three years, if sustained, they may have relevant effects on population health.’
The study found other benefits from omega-3s too, including a 10 percent lower rate of falls and 13 percent fewer infections in older people. ‘This is the biggest trial we have today that hints that a simple supplement contributes to slowing biological ageing’, concluded Bischoff-Ferrari.
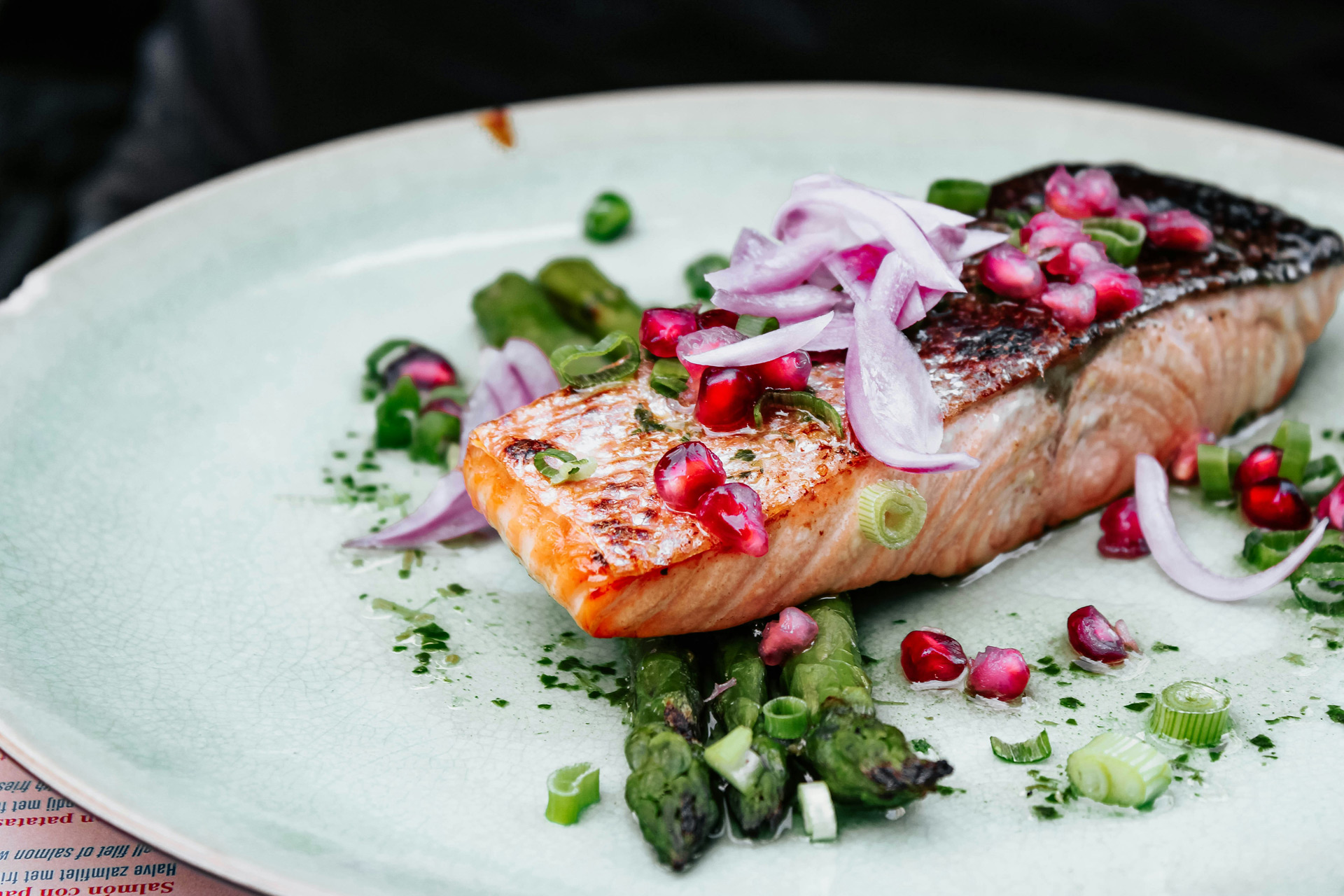
Which Foods Are High In Omega-3?
Omega-3s are polyunsaturated fats that perform important functions in the body. As the body can’t produce them on their own, it’s crucial we get them from our diet. You’ll find them in foods such as:
- Oily fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines and anchovies
- White fish like sea bream and halibut
- Seeds including flaxseeds and chia seeds
- Nuts including walnuts and macadamias
- Beans including kidney beans and edamame

Unsplash
Although there are no official guidelines, the NHS recommends people eat at least two 140g of fish per week, including one portion of oily fish. If you’re struggling to get enough, omega-3s are also widely available in a supplement known as fish oil – which was used in the aforementioned study.
What Are The Other Benefits Of Omega-3s?
Omega-3 fatty acids offer an abundance of benefits for the body. They have been linked to better heart health, as they lower blood pressure and reduce a type of fat in the blood called triglycerides (high levels improve your chances of having a heart attack). Research has also found this key nutrient can support eye and brain health, as well as improving bone health – therefore reducing your risk of osteoporosis.
The perks aren’t just physical either: fish oil can also boost mental health, with one study finding eating moderate amounts of fish with omega-3s reduces your risk of depression.