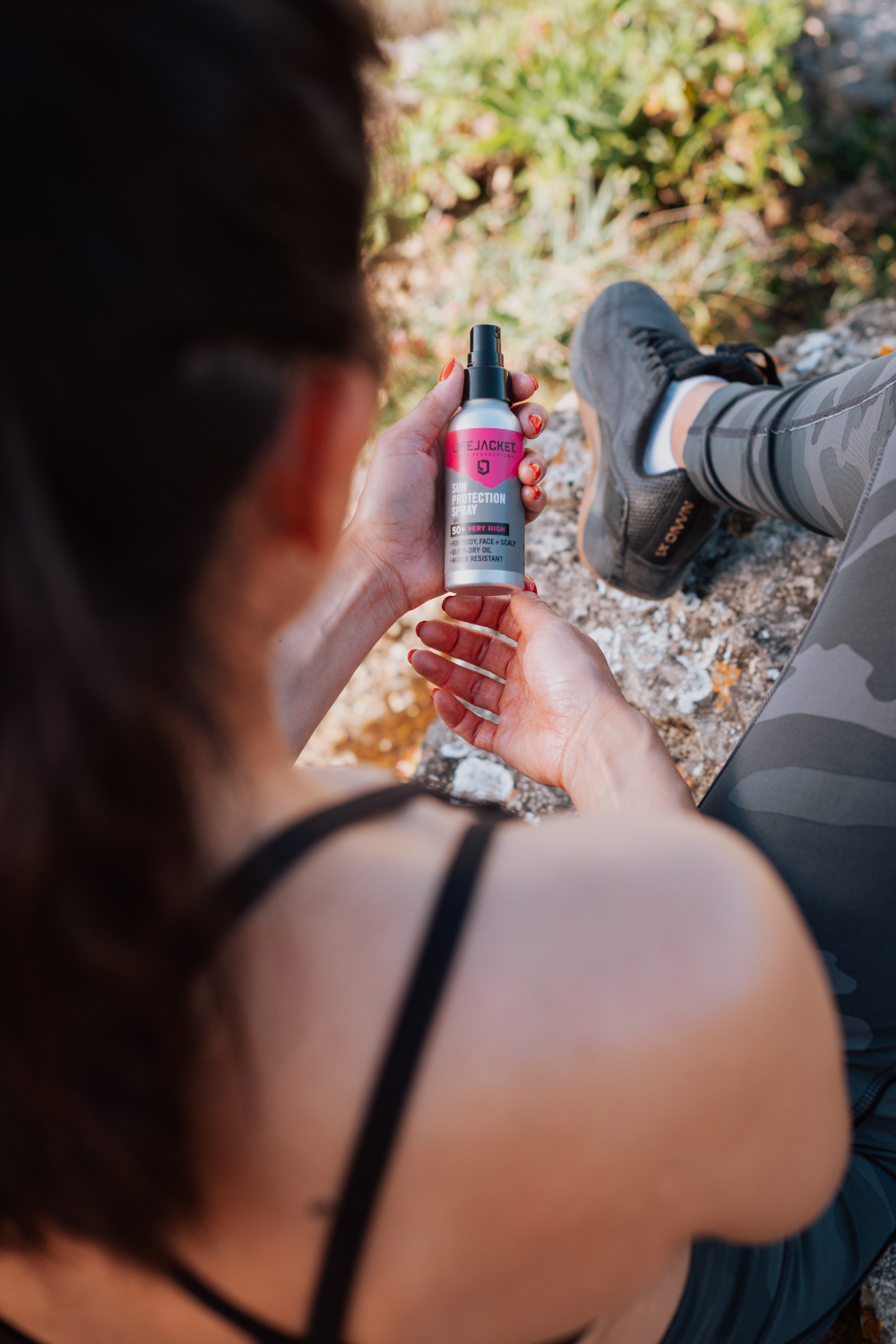
Ask The Expert: Do You Need To Apply Sunscreen Everyday?
By
8 months ago
Spoiler, it's a 'yes'
With summer now in full swing (finally), you’ll find us out in the park, at the pub or simply strolling through the city taking in the glorious weather. And the crowning glory of our skincare routine? Suncare, of course. Before settling into the season, we ask Jono Sumner, a Co-Founder of LifeJacket, everything we need to know to keep our skin protected.
A Guide To Proper Suncare (& The Myths To Avoid)
What are UV rays?
Exactly like light, Ultra Violet (UV) rays are emitted by the sun. There are two types that reach us, UVA and UVB (with UVC rays being filtered out by the earth’s atmosphere). Without sufficient protection, these rays penetrate the skin’s surface, in turn damaging DNA and proteins that perform a range of functions which keep our skin healthy.
How does sunscreen help protect our skin?
Any sun protection product works by preventing UV rays from penetrating the skin and causing damage as outlined above. There are two methods of achieving this protection: chemical and physical. Chemical works when UV filters (the ingredients that do the important job of defending against UV rays) that are applied to the skin absorb UV rays, converting them into harmless heat energy. Physical protection works like a suit of arms, sitting on top of the skin and deflecting UV rays before they reach the skin’s surface. One is not better than the other. It all boils down to your skin, personal preference and what you are doing when UV protection is needed.

What should we look out for when choosing sunscreen?
Sun Protection Factor (SPF) represents how much protection a given product offers against UVB rays (UVB rays being strongest during the summer months, but only accounting for five percent of all UV that reaches us), with a higher SPF value offering UVB protection for longer.
UVA (which is present all year round and accounts for the other 95 percent of all UV we are exposed to) protection is represented by a mix of standards, including the star system in the UK, UVA circle in Europe and PA+ system elsewhere.
We always recommend using a product that offers broad spectrum protection (so protection against both UVA and UVB rays), with high SPF and UVA values.
How much sunscreen should we apply to our face and body?
The level of UV protection claimed by a suncare product is based on the assumption you are using 5ml (a teaspoon) of product per body part – and we have seven body parts: two arms, two legs, back, front and head. Using less than this means you will be getting less protection than the product claims or offers. How much you should use will depend on a number of variables, including skin type, the environment you are in and what you are doing at the time.
And how often should we reapply?
There is no hard and fast rule, as how at-risk you are depends on a number of factors. Most skin damage occurs because people overestimate how protected they are or underestimate how exposed to UV they are, so our advice is always, if in any doubt, reapply regularly (every few hours). Better safe than sorry.

What about aftersun care – which ingredients are best for treating skin after too much sun exposure?
The first thing to say here is that aftersun products do not undo damage caused by overexposure to UV. These products work by helping to cool and soothe dry, damaged or irritated skin, but it is all about reducing discomfort as opposed to reversing damage. So any product that achieves this and helps return water to the skin (which is what moisturisers are all about) will be well received.
Do we really need to apply sunscreen everyday?
The single best thing you can do for the short, medium and long term health of your skin is protect it from UV every single day, 365 days a year. So, incorporate an SPF product into your daily routine. Beyond that, please don’t underestimate the risks and, if in any doubt, err on the side of caution. The benefits may not be immediately apparent, but your skin will thank you in the years to come.
Fact Or Myth: Suncare Edition
The sun and its UV rays are strongest when it’s hottest.
Partly true! UVB rays are strongest when the sun is highest in the sky, so in summer and during the middle of the day. Whilst there is a strong correlation between temperature and UVB levels, it is not exact, so variables like altitude and proximity to the equator have an impact. If in doubt, check the UV index on your phone’s weather app and please don’t forget that UVA rays are equally present all year round – which is why we are huge advocates of the importance and benefit of protecting your skin from UV everyday.
People with darker skin don’t get sunburnt.
False. Those with darker skin have higher natural levels of melanin, the pigment that dictates our skin colour and which acts as our bodies natural defence against UV (a tan is our body releasing melanin to defend against excess UV exposure). That said, we can all get sunburnt if we are exposed to more UV than our body can naturally handle. Please remember, there is no such thing as a healthy tan, a tan is simply our body’s way of telling us it is under attack and getting damaged.

You need as much sun as possible to get enough vitamin D.
False. Our body actually needs relatively little UV exposure, which we will get incidentally, to help synthesise the required levels of Vitamin D.
You can’t get sunburnt on cloudy days.
False. There are a number of factors that can lower our perception of the risks of UV exposure, including temperature, wind and clouds. But even though we may not be able to see the sun, we are still very much exposed to UV.
Sunscreen is the only way to protect yourself from too much sun.
False. Beyond the various different sunscreens, Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) clothing is a fantastic option. A typical cotton t-shirt offers the equivalent of only ~SPF5, so UV rays will still be reaching and penetrating your skin. UPF clothing offers a far higher level of protection (LifeJacket’s clothing is UPF50+, for example) so is certainly a good alternative.

Aftersun products repair the damage done by sunburn.
False. No aftersun product will undo the damage caused by excess UV exposure. They are simply about reducing soreness and irritation by helping to cool and soothe and return moisture to the skin.
The sun in the UK isn’t strong enough to give me sunburn
False. A number of factors can cause us to lower our guard when it comes to how exposed we are, including wind, temperature and clouds and our perception of the environment we are in. The sun in the UK is absolutely strong enough to cause sunburn, so please don’t underestimate it.
About The Expert
Jono Sumner is one of the Co-Founders of LifeJacket, a UK skin protection brand on a mission to halt the increase in skin cancer. With skin cancer rates having doubled in the last 20 years – with forecasts suggesting the number will double again in the next 20 – Jono and the LifeJacket team want to lead the way in helping people protect their short, medium and long term skin health. lifejacketskin.com
Images courtesy of LifeJacket